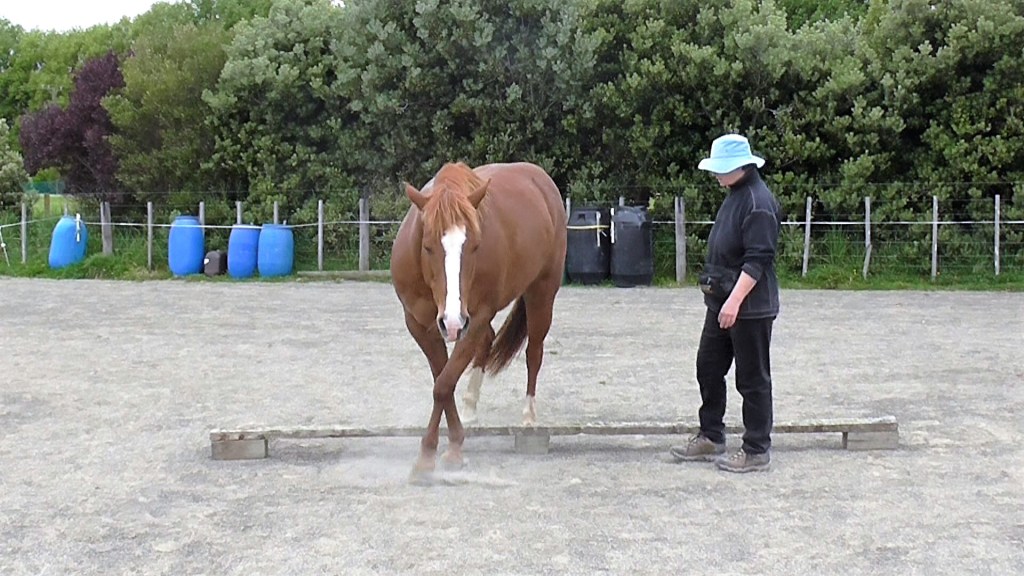
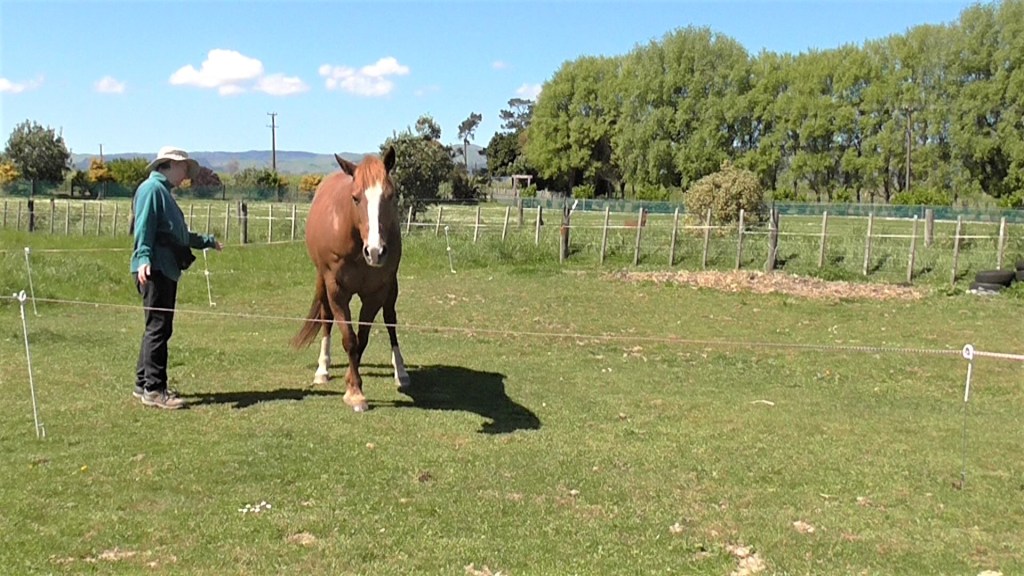
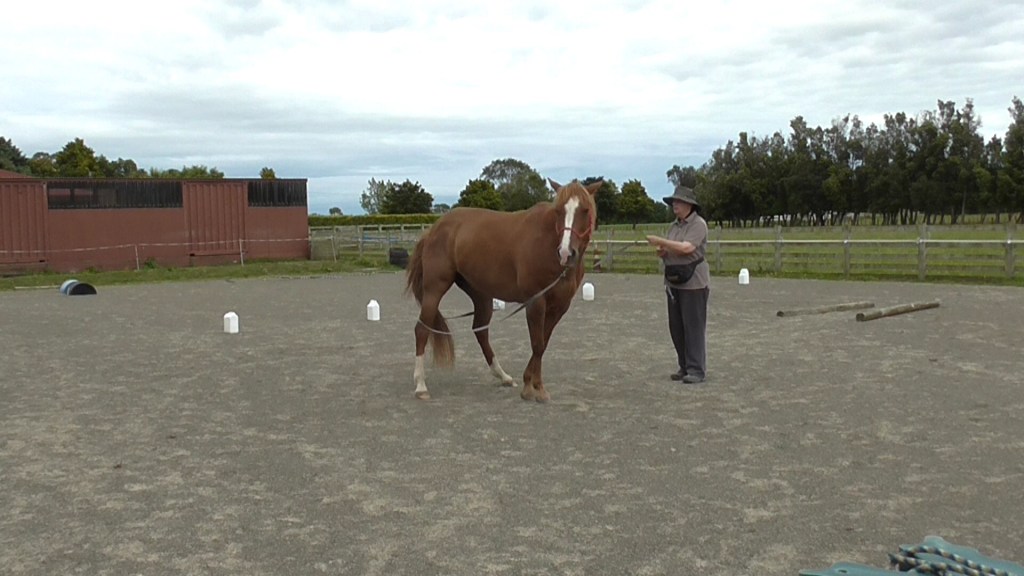
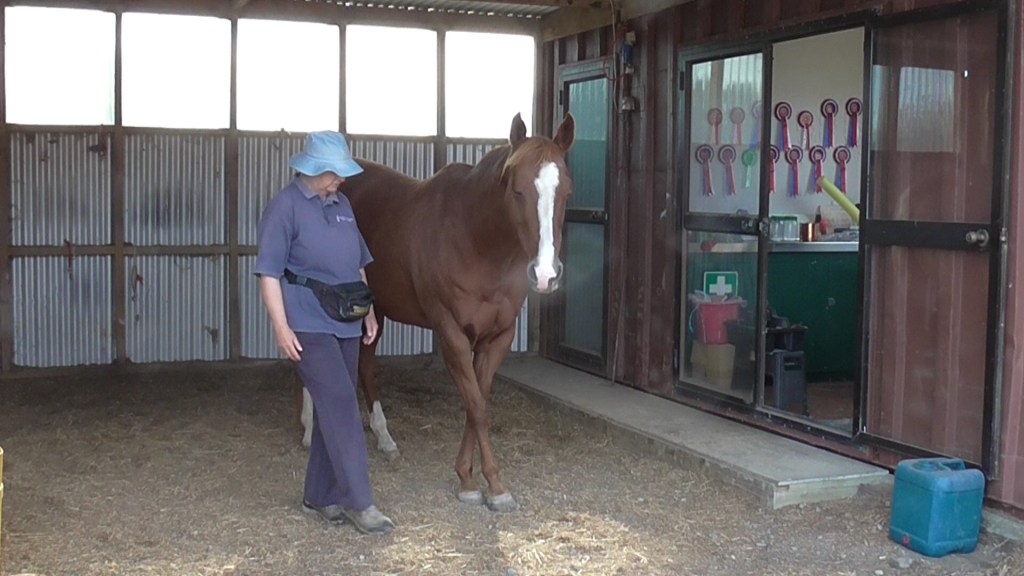
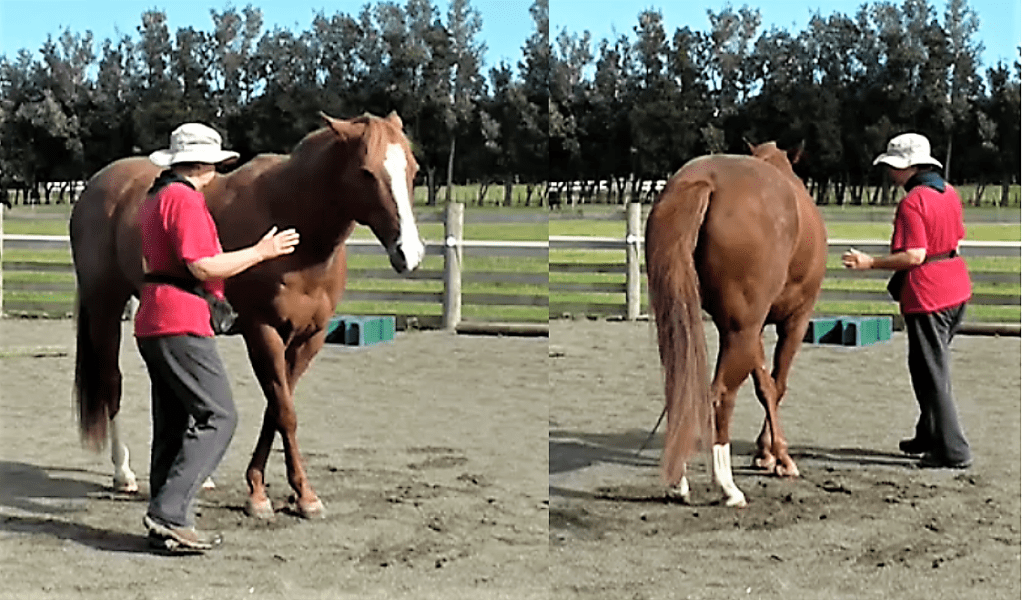
In the photo above, Bridget can FEEL that Boots is relaxed enough for her to carry on with foot care.
Feel is an aspect of horsemanship that sometimes seems elusive, but it doesn’t have to be. It is closely linked with the idea of empathy. Empathy itself is the ability to ‘feel’ what another being is probably feeling.
When dealing with horses, empathy and feel are involved with everything we do. The more we understand about the nature of horses as a prey species that depends on rapid moving away from danger and group life for security, the more empathetic we can be when our horse shows us that he is uncomfortable about something we are asking him to do.
The more we understand that the horse’s digestive system is geared toward a steady flow of low nutrient forage, the better job we can do at providing such forage. We know that to keep the horse comfortable, we must feed the bacteria in the gut in a way that keeps them happy.

Horse have evolved to reqire a constant supply of low-energy forage to keep their microbiome in good working condition.
Horses have small stomachs and a large caecum where bacteria break down the food so it can be absorbed by the horse. These bacteria need a constant flow of food and do not like sudden changes of diet.
The more we understand how the horse’s circulation system depends on slow, regular walking movement over 24 hours, the less inclined we will be to confine horses in boxes. After all, they are not chocolates.
The horse’s feet compress and expand with each step the horse takes. Foot movements work like four extra pumps to help send blood the very long way up the legs back to the heart.
Horses step along as they graze. The only time they are still is for the few hours that they sleep, which are spread over 24 hours. Consistent movement is an integral part of horse circulation health.
Horses are naturally active on a 24-hour rhythm, not a day/night rhythm like we are. By ‘putting them in at night’ and by ‘feeding them meals’ in one place, we are seriously mucking about with their movement, their blood circulation and their natural biorhythms.
Many horse ‘problems’ stem from unnatural housing and unnatural feeding regimes as well as the damage caused by nailing inflexible steel shoes to a dynamic live foot mechanism.
As we develop empathy and ‘feel’ about what a horse is experiencing in the strange human-based world in which he finds himself, it becomes easier to know what we should do to ensure the horse is as comfortable as possible.
A horse high on adrenalin will find comfort in being allowed to trot or run the adrenalin out of his system. When he becomes high-headed and agitated, a handler with feel gives him the opportunity to move until he can switch from reactive mode to responsive mode.
A strong-spirited, low-energy horse can be extremely frustrating. A handler with feel for this sort of horse will use click&treat motivation as much as possible. Then it is easier to appreciate the reliable nature of this type of horse once he is on-side with the handler rather than trying to outwit him or her.
As soon as we can see our horse, he can see us. As soon as he can see us, he is gauging our energy level. He is ‘feeling’ us. A person with ‘feel’ will be doing the same with the horse – gauging his mood, the way he is moving or grazing, checking for anything out of the ordinary.

As soon as a horse sees us, he is feeling our mood, our energy level and our intent.
When a handler develops ‘feel’ of this sort, s/he is not frustrated by undesirable horse behaviors. S/he seeks the cause(s) and adjusts the horse’s lifestyle plus his Individual Education Program (IEP) to accommodate the horse. This is the essence of a handler’s emotional neutrality.
Horses don’t do things just to annoy us. At any moment in time the horse is doing what he believes is the best thing do.
With careful education, we can enlarge the horse’s comfort zone and areas of expertise. We can expand his repertoire of things he can do with confidence.
It takes considerable time and effort, but done at the horse’s pace, he will gain skills to help him through his whole life.
27-1: Some concepts of ‘feel’
‘Feel’ comes in many guises. Here are some of them.
- Feeling the difference between reaction and response
- Realizing that every horse will feel different, and that to the horse, each handler feels different
- Knowing the precise moment to release signal pressure (click&treat)
- Acknowledging the difference between teaching and forcing
- Knowing when we are pushing too much, resulting in a loss of willingness
- Knowing when we are pausing too much, resulting in a loss of interest
- Recognizing physical well-being, so that lack of wellness stands out
- Finding the ‘balance’ between the two extremes of ‘unbalanced’
- Able to cause a subtle shift in the horse so he regains balance
- Staying grounded when the horse loses his physical, mental and/or emotional balance
- Able to pause for lesson absorption or for a shift in balance
- Able to ignore unwanted behavior and quietly ‘re-set’ a task
- Understanding a specific horse’s underlying character type
- Recognizing when the horse is ready to move on to the next slice of the new learning
- Recognizing when the horse-human connection is present and when it is absent
- Not taking the horse’s trust for granted
- Understanding the lives of horses in the wild; their natural 24 hour and seasonal rhythms
- Understanding physical, mental and emotional thresholds of a specific horse
- Understanding how habituation works
- Understanding how desensitization works
- Understanding how sensitization works
- Physical feel through the rope
- Physical feel through the reins
- Physical and emotional feel through the whole body when riding
- Feel for two-way communication playing at liberty. If the horse decides to leave, knowing how to motivate him to join up again or deciding to call it a day
- Knowing when to stop a session, or a part within the session
- Understanding that the way the handler feels is instantly picked up by the horse, good feelings and bad feelings equally.